Van Allen radiation belt
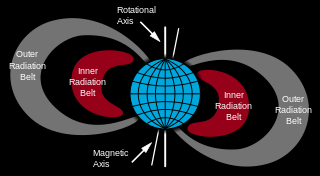
A Van Allen radiation belt is a zone of energetic charged particles , most of which originate from the solar wind , that are captured by and held around a planet by that planet's magnetic field . Earth has two such belts and sometimes others may be temporarily created. The discovery of the belts is credited to James Van Allen , and as a result, Earth's belts are known as the Van Allen belts . Earth's two main belts extend from an altitude of about 500 to 58,000 km (310 to 36,040 mi) [1] above the surface in which region radiation levels vary. Most of the particles that form the belts are thought to come from solar wind and other particles by cosmic rays . [2] By trapping the solar wind, the magnetic field deflects those energetic particles and protects the atmosphere from destruction.
Page Revisions
| Year | Metadata | Sections | Top Words | First Paragraph |
| 2018 |
119290 characters 14 sections 35 paragraphs 11 images 194 internal links 72 external links |
belts 0.539 allen 0.348 van 0.278 belt 0.230 radiation 0.209 flux 0.160 particles 0.155 inner 0.149 electrons 0.147 mev 0.139 energetic 0.124 outer 0.113 geomagnetic 0.107 magnetic 0.106 antiprotons 0.105 |
A Van Allen radiation belt is a zone of energetic charged particles , most of which originate from the solar wind , that are captured by and held around a planet by that planet's magnetic field . Earth has two such belts and sometimes others may be temporarily created. The discovery of the belts is credited to James Van Allen , and as a result, Earth's belts are known as the Van Allen belts . Earth's two main belts extend from an altitude of about 500 to 58,000 km (310 to 36,040 mi) [1] above the surface in which region radiation levels vary. Most of the particles that form the belts are thought to come from solar wind and other particles by cosmic rays . [2] By trapping the solar wind, the magnetic field deflects those energetic particles and protects the atmosphere from destruction. |
|
| 2017 |
116115 characters 14 sections 34 paragraphs 11 images 184 internal links 65 external links |
belts 0.545 allen 0.352 van 0.281 belt 0.226 radiation 0.211 flux 0.162 inner 0.151 particles 0.150 electrons 0.148 mev 0.140 energetic 0.126 outer 0.115 geomagnetic 0.109 magnetic 0.100 protons 0.096 |
A Van Allen radiation belt is a zone of energetic charged particles , most of which originate from the solar wind that is captured by and held around a planet by that planet's magnetic field . The Earth has two such belts and sometimes others may be temporarily created. The discovery of the belts is credited to James Van Allen , and as a result the Earth's belts are known as the Van Allen belts . Earth's two main belts extend from an altitude of about 500 to 58,000 kilometers [1] above the surface in which region radiation levels vary. Most of the particles that form the belts are thought to come from solar wind and other particles by cosmic rays . [2] By trapping the solar wind, the magnetic field deflects those energetic particles and protects the Earth's atmosphere from destruction. |
|
| 2016 |
114331 characters 14 sections 36 paragraphs 11 images 184 internal links 62 external links |
belts 0.548 allen 0.340 van 0.272 belt 0.227 radiation 0.212 flux 0.163 inner 0.152 particles 0.151 electrons 0.149 mev 0.141 energetic 0.126 geomagnetic 0.125 outer 0.115 magnetic 0.101 protons 0.097 |
A radiation belt is a zone of energetic charged particles , most of which originate from the solar wind that is captured by and held around a planet by that planet's magnetic field . The Earth has two such belts and sometimes others may be temporarily created. The discovery of the belts is credited to James Van Allen , and as a result the Earth's belts are known as the Van Allen belts . Earth's two main belts extend from an altitude of about 1,000 to 60,000 kilometers above the surface in which region radiation levels vary. Most of the particles that form the belts are thought to come from solar wind and other particles by cosmic rays . [1] By trapping the solar wind, the magnetic field deflects those energetic particles and protects the Earth's atmosphere from destruction. |
|
| 2015 |
110045 characters 13 sections 34 paragraphs 10 images 174 internal links 61 external links |
belts 0.548 allen 0.325 van 0.260 belt 0.234 radiation 0.199 inner 0.195 electrons 0.172 particles 0.151 mev 0.141 outer 0.133 flux 0.130 energetic 0.126 geomagnetic 0.125 protons 0.110 magnetic 0.086 |
A radiation belt is a layer of energetic charged particles that is held in place around a magnetized planet, such as the Earth, by the planet's magnetic field . The Earth has two such belts and sometimes others may be temporarily created. The discovery of the belts is credited to James Van Allen and as a result the Earth's belts are known as the Van Allen belts . The main belts extend from an altitude of about 1,000 to 60,000 kilometers above the surface in which region radiation levels vary. Most of the particles that form the belts are thought to come from solar wind and other particles by cosmic rays . [1] The belts are located in the inner region of the Earth's magnetosphere . The belts contain energetic electrons that form the outer belt and a combination of protons and electrons that form the inner belt. Other nuclei, such as alpha particles , are less prevalent. The belts endanger satellites , which must protect their sensitive components with adequate shielding if they spend significant time in the radiation belts. In 2013, NASA reported that the Van Allen Probes had discovered a transient, third radiation belt, which was observed for four weeks until destroyed by a powerful, interplanetary shock wave from the Sun . [2] |
|
| 2014 |
111774 characters 13 sections 36 paragraphs 11 images 179 internal links 59 external links |
belts 0.528 allen 0.327 van 0.262 belt 0.249 radiation 0.239 inner 0.174 electrons 0.173 particles 0.152 mev 0.142 flux 0.131 energetic 0.127 geomagnetic 0.126 outer 0.122 protons 0.111 magnetic 0.087 |
A radiation belt is a layer of energetic charged particles that is held in place around a magnetized planet, such as the Earth, by the planet's magnetic field . The Earth has two such belts and sometimes others may be temporarily created. The discovery of the belts is credited to James Van Allen and as a result the Earth's belts bear his name. The main belts extend from an altitude of about 1,000 to 60,000 kilometers above the surface in which region radiation levels vary. Most of the particles that form the belts are thought to come from solar wind and other particles by cosmic rays . [1] The belts are located in the inner region of the Earth's magnetosphere . The belts contain energetic electrons that form the outer belt and a combination of protons and electrons that form the inner belt. The radiation belts additionally contain lesser amounts of other nuclei, such as alpha particles . The belts endanger satellites , which must protect their sensitive components with adequate shielding if their orbit spends significant time in the radiation belts. In 2013, NASA reported that the Van Allen Probes had discovered a transient, third radiation belt, which was observed for four weeks until destroyed by a powerful, interplanetary shock wave from the Sun . [2] |
|
| 2013 |
102370 characters 13 sections 32 paragraphs 9 images 175 internal links 52 external links |
belts 0.488 allen 0.380 van 0.304 radiation 0.255 belt 0.236 electrons 0.160 mev 0.151 particles 0.142 flux 0.140 inner 0.140 geomagnetic 0.134 protons 0.118 outer 0.117 energetic 0.111 antiprotons 0.091 |
A Van Allen radiation belt is one of at least two layers of energetic charged particles ( plasma ) that is held in place around the planet Earth by the planet's magnetic field . The belts extend from an altitude of about 1,000 to 60,000 kilometers above the surface in which region radiation levels vary. Most of the particles that form the belts are thought to come from solar wind and other particles by cosmic rays . [1] The belts are named after their discoverer, James Van Allen , and are located in the inner region of the Earth's magnetosphere . The belts contain energetic electrons that form the outer belt and a combination of protons and electrons that form the inner belt. The radiation belts additionally contain lesser amounts of other nuclei, such as alpha particles . The belts endanger satellites , which must protect their sensitive components with adequate shielding if their orbit spends significant time in the radiation belts. In 2013, NASA reported that the Van Allen Probes had discovered a transient, third radiation belt, which was observed for four weeks until destroyed by a powerful, interplanetary shock wave from the Sun . [2] |
|
| 2012 |
86587 characters 12 sections 33 paragraphs 9 images 157 internal links 34 external links |
belts 0.472 allen 0.344 van 0.275 radiation 0.261 belt 0.255 electrons 0.173 particles 0.160 inner 0.159 flux 0.151 geomagnetic 0.144 protons 0.128 mev 0.122 energetic 0.120 outer 0.119 antiprotons 0.098 |
The Van Allen radiation belt is composed of two torus -shaped layers of energetic charged particles ( plasma ) around the planet Earth, held in place by its magnetic field. The belt extends from an altitude of about 1,000 to 60,000 kilometres above the surface, in which region radiation levels vary. It is thought that most of the particles that form the belts come from solar wind , and other particles by cosmic rays . [1] It is named after its discoverer, James Van Allen , and is located in the inner region of the Earth's magnetosphere . It is split into two distinct belts, with energetic electrons forming the outer belt and a combination of protons and electrons forming the inner belt. In addition, the radiation belts contain lesser amounts of other nuclei, such as alpha particles . The belts pose a hazard to satellites, which must protect their sensitive components with adequate shielding if their orbit spends significant time in the radiation belts. |
|
| 2011 |
67147 characters 12 sections 30 paragraphs 7 images 150 internal links 28 external links |
belts 0.526 radiation 0.282 allen 0.274 belt 0.231 van 0.219 electrons 0.178 flux 0.168 geomagnetic 0.161 particles 0.154 mev 0.136 energetic 0.133 protons 0.124 inner 0.112 outer 0.110 magnetic 0.093 |
The Van Allen radiation belt is a torus of energetic charged particles ( plasma ) around Earth, which is held in place by Earth's magnetic field . It is believed that most of the particles that form the belts come from solar wind , and other particles by cosmic rays . [1] It is named after its discoverer, James Van Allen , and is located in the inner region of the Earth's magnetosphere . It is split into two distinct belts, with energetic electrons forming the outer belt and a combination of protons and electrons forming the inner belts. In addition, the radiation belts contain lesser amounts of other nuclei, such as alpha particles . The belts pose a hazard to satellites, which must protect their sensitive components with adequate shielding if their orbit spends significant time in the radiation belts. |
|
| 2010 |
60326 characters 11 sections 31 paragraphs 7 images 159 internal links 17 external links |
belts 0.501 belt 0.268 radiation 0.259 allen 0.247 electrons 0.201 van 0.198 geomagnetic 0.189 protons 0.167 particles 0.160 energetic 0.139 flux 0.131 magnetic 0.126 outer 0.122 mev 0.118 inner 0.107 |
The Van Allen radiation belt is a torus of energetic charged particles ( plasma ) around Earth , which is held in place by Earth's magnetic field . These high-energy charged particles result from cosmic rays . The earth's magnetic field is not uniformly distributed around the Earth. On the sunward side, it is compressed because of the solar wind , while on the other side it is elongated to around three earth radii. |
|
| 2009 |
52189 characters 9 sections 23 paragraphs 6 images 147 internal links 14 external links |
belts 0.475 belt 0.270 electrons 0.252 allen 0.244 radiation 0.242 geomagnetic 0.196 van 0.195 protons 0.194 energetic 0.162 particles 0.158 mev 0.138 outer 0.124 resp 0.111 inner 0.102 magnetic 0.102 |
The Van Allen radiation belt is a torus of energetic charged particles ( plasma ) around Earth , which is held in place by Earth's magnetic field . This field is not uniformly distributed around the Earth. On the sunward side, it is compressed because of the solar wind , while on the other side it is elongated to around three earth radii. This creates a cavity called the Chapman Ferraro Cavity, in which the Van Allen radiation belt resides. It is split into two distinct belts, with energetic electrons forming the outer belt and a combination of protons and electrons creating the inner belt. In addition, the belts contain lesser amounts of other nuclei, such as alpha particles . The Van Allen belts are closely related to the polar aurora where particles strike the upper atmosphere and fluoresce . |
|
| 2008 |
42766 characters 9 sections 22 paragraphs 3 images 150 internal links 9 external links |
belts 0.486 allen 0.295 belt 0.254 radiation 0.237 van 0.236 geomagnetic 0.225 electrons 0.221 protons 0.177 energetic 0.166 particles 0.141 outer 0.117 magnetic 0.104 ions 0.101 field 0.097 trapped 0.090 |
The Van Allen radiation belt is a torus of energetic charged particles ( plasma ) around Earth , held in place by Earth's magnetic field . Earth's geomagnetic field is not uniformly distributed around its surface. On the sun side, it is compressed because of the solar wind and on the other side, it is elongated to around three earth radii. This creates a cavity called the Chapman Ferraro Cavity, in which the Van Allen radiation belts reside. The Van Allen belts are closely related to the polar aurora where particles strike the upper atmosphere and fluoresce . |
|
| 2007 |
32687 characters 9 sections 22 paragraphs 4 images 112 internal links 5 external links |
belts 0.528 allen 0.308 van 0.247 belt 0.231 radiation 0.205 electrons 0.192 protons 0.185 geomagnetic 0.183 energetic 0.173 particles 0.137 outer 0.112 magnetic 0.109 ions 0.106 mev 0.089 particle 0.088 |
The Van Allen Radiation Belt is a torus of energetic charged particles ( plasma ) around Earth , held in place by Earth's magnetic field . The Van Allen belts are closely related to the polar aurora where particles strike the upper atmosphere and fluoresce . |
|
| 2006 |
31308 characters 8 sections 21 paragraphs 3 images 101 internal links 5 external links |
belts 0.551 allen 0.323 van 0.258 belt 0.213 radiation 0.210 protons 0.180 energetic 0.168 electrons 0.168 geomagnetic 0.152 particles 0.143 magnetic 0.117 outer 0.109 inner 0.094 mev 0.086 particle 0.086 |
The Van Allen Radiation Belt is a torus of energetic charged particles ( plasma ) around Earth , held in place by Earth's magnetic field . The Van Allen belts are closely related to the polar aurora where particles strike the upper atmosphere and fluoresce . |
|
| 2005 |
20645 characters 7 sections 17 paragraphs 2 images 87 internal links 3 external links |
2. The Van Allen Belt's impact on space travel |
belts 0.509 belt 0.345 radiation 0.267 allen 0.247 van 0.198 particles 0.178 outer 0.172 electrons 0.125 ions 0.115 inner 0.110 trapped 0.103 magnetic 0.094 gap 0.092 waves 0.087 explorer 0.086 |
The Van Allen radiation belt is a torus of energetic charged particles (ie. a plasma ) around Earth , trapped by Earth's magnetic field . When the belts "overload", particles strike the upper atmosphere and fluoresce , causing the polar aurora . The presence of a radiation belt had been theorized prior to the Space Age and the belt's presence was confirmed by the Explorer I on January 31 , 1958 and Explorer III missions, under Doctor James Van Allen . The trapped radiation was first mapped out by Explorer IV and Pioneer III . |
| 2004 |
26702 characters 9 sections 30 paragraphs 1 images 98 internal links 5 external links |
3. Radial Diffusion Induced by Magnetic Fluctuations 4. The Van Allen Belt's Impact on Space Travel 6. The Van Allen Belts and Why They Exist |
belts 0.413 belt 0.345 elevator 0.294 radiation 0.285 shielding 0.263 allen 0.209 van 0.167 protons 0.142 ions 0.140 outer 0.134 particles 0.130 electrons 0.119 inner 0.117 trapped 0.111 magnetic 0.106 |
The Van Allen radiation belt is a torus of energetic charged particles around Earth , trapped by Earth's magnetic field . When the belts "overload", particles strike the upper atmosphere and fluoresce , causing the polar aurora . The presence of a radiation belt had been theorized prior to the Space Age and the belt's presence was confirmed by the Explorer I on January 31 , 1958 and Explorer III missions, under Doctor James van Allen . The trapped radiation was first mapped out by Explorer IV and Pioneer III . |
| 2003 |
19099 characters 8 sections 21 paragraphs 0 images 92 internal links 2 external links |
3. Radial Diffusion Induced by Magnetic Fluctuations 4. The Van Allen Belt's Impact on Space Travel |
belt 0.436 belts 0.429 radiation 0.289 ions 0.193 allen 0.173 particles 0.167 electrons 0.164 outer 0.161 trapped 0.154 explorer 0.141 protons 0.141 van 0.139 inner 0.133 intensity 0.098 iii 0.091 |
The Van Allen radiation belt is a torus of energetic charged particles around Earth , trapped by Earth's magnetic field . When the belts "overload", particles strike the upper atmosphere and fluoresce ; causing the polar aurora . The presence of a radiation belt had been theorized prior to the Space Age and the belt's presence was confirmed by the Explorer I on January 31 , 1958 and Explorer III missions, under Doctor James Van Allen . The trapped radiation was first mapped out by Explorer IV and Pioneer III . |
| 2002 |
18471 characters 8 sections 24 paragraphs 0 images 87 internal links 2 external links |
3. Radial Diffusion Induced by Magnetic Fluctuations 4. The Van Allen Belt's Impact on Space Travel |
belt 0.444 belts 0.413 radiation 0.295 ions 0.197 allen 0.177 electrons 0.167 outer 0.164 particles 0.157 trapped 0.157 explorer 0.144 protons 0.144 van 0.141 inner 0.135 intensity 0.100 iii 0.093 |
The Van Allen radiation belt is a torus of energetic charged particles around Earth , trapped by Earth's magnetic field . The presence of a radiation belt had been theorized prior to the Space Age and the belt's presence was confirmed by the Explorer I and Explorer III missions, under Doctor James Van Allen . The trapped radiation was first mapped out by Explorer IV and Pioneer III . |